Ions
Atom is electrically neutral. When it loses or gains electron, it becomes ion.Ions are the atom or a group of atoms with electrical charge.
In the following picture, how sodium cation is made from sodium atom. This is achieved by losing the valence electron of sodium atom.
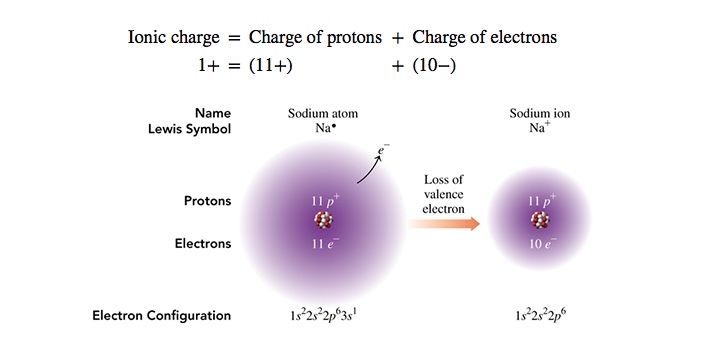
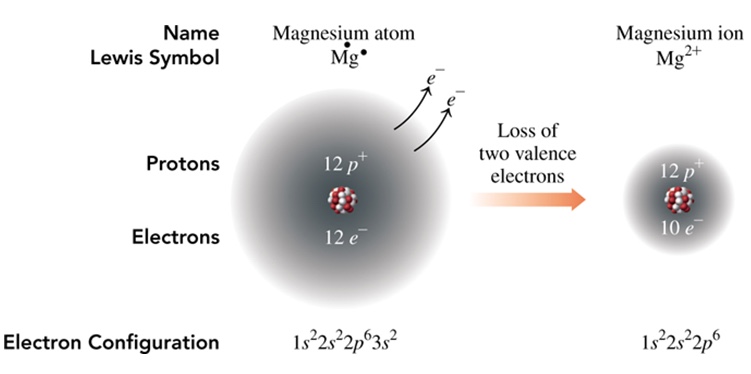
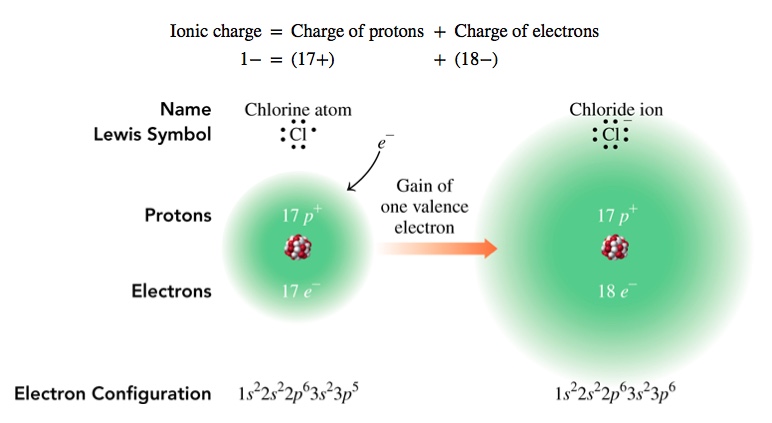
Naming of Ions
Groups 1 and 2 - Either +1 and +2 ions - in these cases, the name is the name of the element. For example, Mg2+ is magnesium ion.
Groups 15, 16, and 17 - They are, respectively, -3, -2 and -1 ions. We add -ide to the name of the element. For example, O2- is oxide ion. And, Br1- is bromide ion.
In the transition metals, nearly all are cations, there are several ionic forms that are available. For example, copper, Cu, has several ionic forms, Cu+1, Cu+2, and Cu+3. They are represented as, respectively, copper(I) ion, copper(II) ion, and copper(III) ion.
There are many polyatomic ions, which contains more than one element in the ion. Here are the list:
| Charge | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| +1 | NH4+ | Ammonium ion |
| -1 | OH- | hydroxide ion |
| -1 | CN- | cyanide ion |
| -2 | CO3-2 | carbonate ion |
| -1 | NO3- | nitrate ion |
| -2 | SO4-2 | sulfate ion |
the Octet Rule
If you recall that elements of Group 1 are likely to become +1 charged ions, and elements of Group 17 are likely to beocome -1 charged. Below is the relationship between group and the charge picked up by the element in each group.| Group | Charge | Example | # protons | # electrons | # valnece electrons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +1 | Na | 11 | 10 | 8 |
| 2 | +2 | Mg | 12 | 10 | 8 |
| 13 | +3 | Al | 13 | 10 | 8 |
| 15 | -3 | N | 7 | 10 | 8 |
| 16 | -2 | O | 8 | 10 | 8 |
| 17 | -1 | F | 9 | 10 | 8 |
| 18 | 0 | Ne | 10 | 10 | 8 |
| 1 | +1 | K | 19 | 18 | 8 |
| 2 | +2 | Ca | 20 | 18 | 8 |
| 15 | -3 | P | 15 | 18 | 8 |
| 16 | -2 | S | 16 | 18 | 8 |
| 17 | -1 | Cl | 17 | 18 | 8 |
| 18 | 0 | Ar | 18 | 18 | 8 |
It means that 8 electrons in the valence shell signifies the stability.
We say that the atoms and ions that has 8 electrons in the valence shell is called octet.
Ionic Compounds
Compound = matter constructed of two or more elements.
Ionic Compounds = Compounds made from ions
Ionic compounds are made of Cation and Anion, but when the compound is made it is electrically neutral!
So, the case of sodium chloride, NaCl
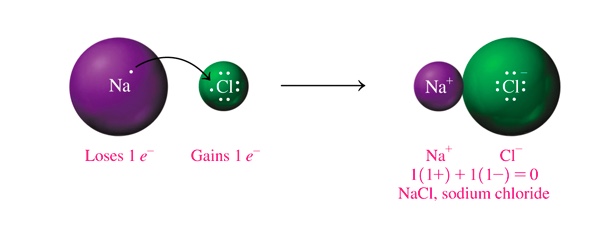
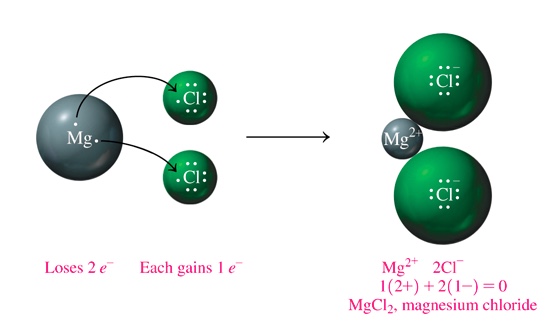
In the case of MgCl2,
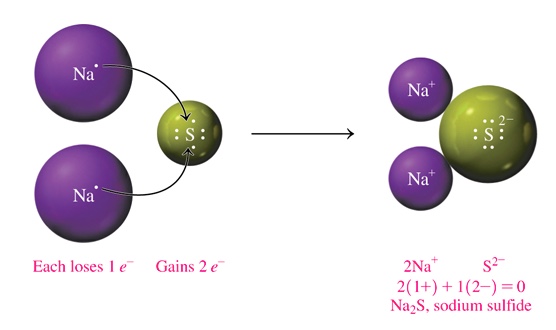
In the following is Na2S.
Naming Ionic Compounds

Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions — ion composed of more than one element.
Often encountered ions are listed in the following table:
| Nonmetal | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | OH- | Hydroxide |
| Nitrogen | NH4+ | Ammonium |
| NO3- | Nitrate | |
| Carbon | CO32- | Carbonate |
| Sulfur | SO42- | Sulfate |
| Phosphorus | PO43- | Phosphate |
Naming of Ions containing polyatomic ions
Exactly the same way we name them. Just remember that the compounds made from ion still has neutral charge!
Al(OH)3 = Aluminum hydroxide
(NH4)2CO3 = Ammonium carbonate
Covalent Bonds
We saw that each group has unique number of valence electrons and we know how to draw them, as shown below: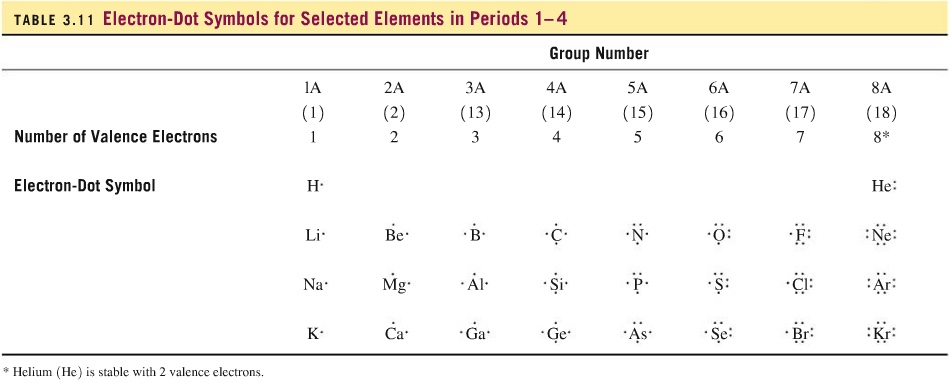
Covalent bond is made by sharing of two electrons between two atoms. So,
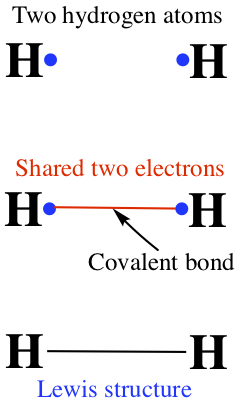
The Lewis structures are important in understanding the properties of molecules.
Let us try drawing a Lewis structure for methane, CH4.
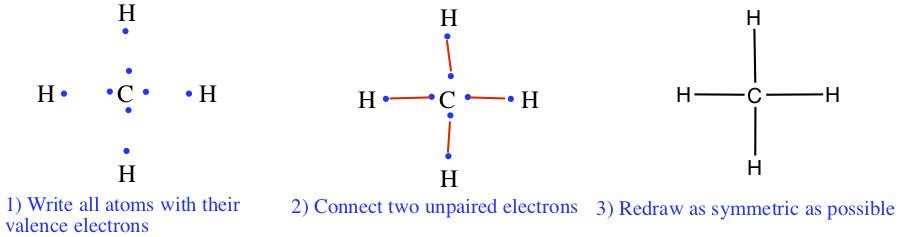
Example: Draw Lewis dot structure of a) phosphorus atom, b) bromine atom, c) barium atom and d) hydrogen atom.
Since phosphorus is group 15 or group 5A, there are five valence electrons. Similarly, bromine is in group 17 or group 7A. Therefore, there are 7 valence electrons. Barium is in group 2 or group 2A and so there are two valence electrons. Hydrogen has only one valence electron since it is in group 1 or group 1A.
| phosphorus | bromine | barium | hydrogen |
|---|---|---|---|
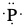 |
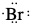 |
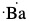 |
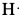 |
Molecules
Covalent compound with no charge overall is called molecule.Naming Binary Molecules
Basically the same as the naming of binary ionic compounds.
The naming of molecular compounds are done in the similar way as we did for ionic compounds. In some cases there are many different numbers of the same elments can exist in molecular compounds, we need to use prefixes to show their numbers.
| Number | Prefix |
|---|---|
| 1 | mono |
| 2 | di |
| 3 | tri |
| 4 | tetra |
| 5 | penta |
| 6 | hexa |
| 7 | hepta |
| 8 | octa |
| 9 | nona |
| 10 | deca |
Formula Weight, Molecular Weight, and Molar Mass
We use Formula Weight, Molecular Weight, and Molar Mass synonymously.Let us calculate molar mass of C6H14 molecule. You need to look at the Periodic Table to see what the masses are. Since the molecule only contains C and H, we have them on the P.T. as
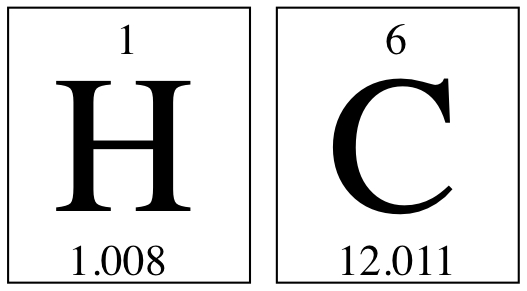
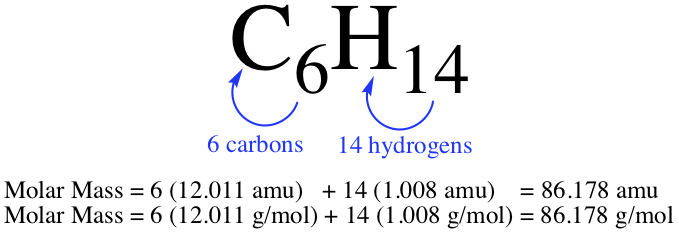
They are the mass of molcule composed of masses of component elements.
If the binary compound is made only of main group elements, it is likely that the compound is binary covalent compound.
If the transition metals are involved, it is likely ionic compound.