Chemistry
Study of "everything" — central science
Study of "change" — your textbook
- Examples:
- drugs
textiles
fabrication of computer chips
metabolism
many many more
My definition: "Study of behavior of e- in atoms and molecules"
Below is a video of biological processes that occur in your body every single seconds of our lives. Each and every particles you see in the video are the molecules of biology. The fundamental inner working of life is definitively chemistry. Many of these images are based on the experimental results of looking into the details of specific biological processes. Pretty amazing stuff!
Traditional Fields of Chemistry
These are dissolving (or smearing) quickly because of collaboration and new research
| Analytical | Quantitation of chemicals — many instrumentations |
| Biochemistry | Study of biological processes |
| Inorganic | Study of molecules containing all but carbon |
| Organic | Study of molecules containing carbon |
| Physical | Understand chemistry through physical means |
Scientific Method
Scientific Method — obtained based upon experiments or observations
Processes in Scinece
Experimental observation → tentative explanation → hypothesis → Law
Law explains empirical facts.
For example. You will learn about gases in Chapter 9. In that chapter, three facts emerge from experiments:
| Observation | English translation of Equation | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| When there are more gas, pressure is increased | Pressure P is proportional to amount n | P ∝ n |
| When temperature is icreased, so as pressure | Pressure P is proportional to temperature T | P ∝ T |
| when gas is compressed, pressure increased | Pressure P is proportional to recipical of volume1/V | P ∝ 1/V |
PV = nRT, Ideal Gas Law
Explains how gases behave.
Two levels of understanding: Law vs. Theory
Law = empirically derived
Theory = explains Law
- Theory explains underlying mechanism at deeper and more fundamental level.
Therefore, colloquial "in theory" is not how we use theory in science. → MUCH DEEPER!
For example: Carbon has 4 bonds → Facts from experiments
Quantum mechanics explains why carbon has 4 bonds.
Classification of Matter
Matter = occupies space and has mass
We can classify Matter into several levels, as shown in the following figure.
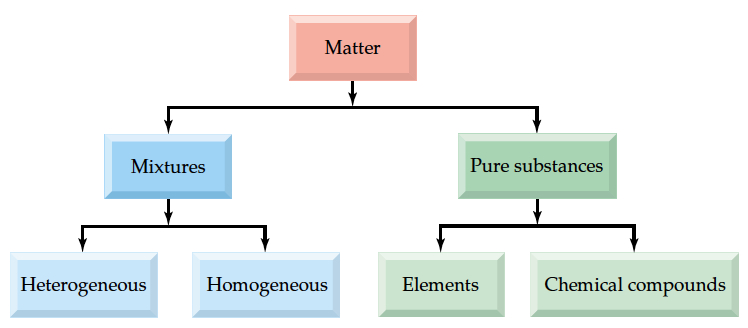
Substance = definite composition and distinct properties
Mixtures consist of Hetergenous and Homogeneous types. Heterogenous mixture is made up of two different and distinct phase separation between substances. For example, oil and vinegar layers of your favorite Italian dressing, have two distinct separation b/w oil layer and aqueous layer. On the other hand, homogenous mixture is like your softdrink before you open the bottle; can not distingush b/w water, sugar, and carbon dioxide, CO2. Furthermore, the sugar and CO2 are distributed throughout the water. Once you open the cap, however, it starts to fizzle, there you created phase separation, in this case you can consider it as heterogenous, but homogenous between water and sugar.
Pure substances can be classified by Elements and Chemical compounds. Chemical compunds are made up of one type of molecules. For example, water is a chemical compound having definite proportion, two Hydrogens and one Oxygen, represented by a chemical formula, H2O.
Chemical Elements
Element (or atom) is the basic building block of chemistry.
Fundamental Substances — chemically unalterable or broken down to simpler substance
Over 90 different naturally occuring elements listed in the Periodic Table of Elements
Usually, we see the periodic table to be in the following way.
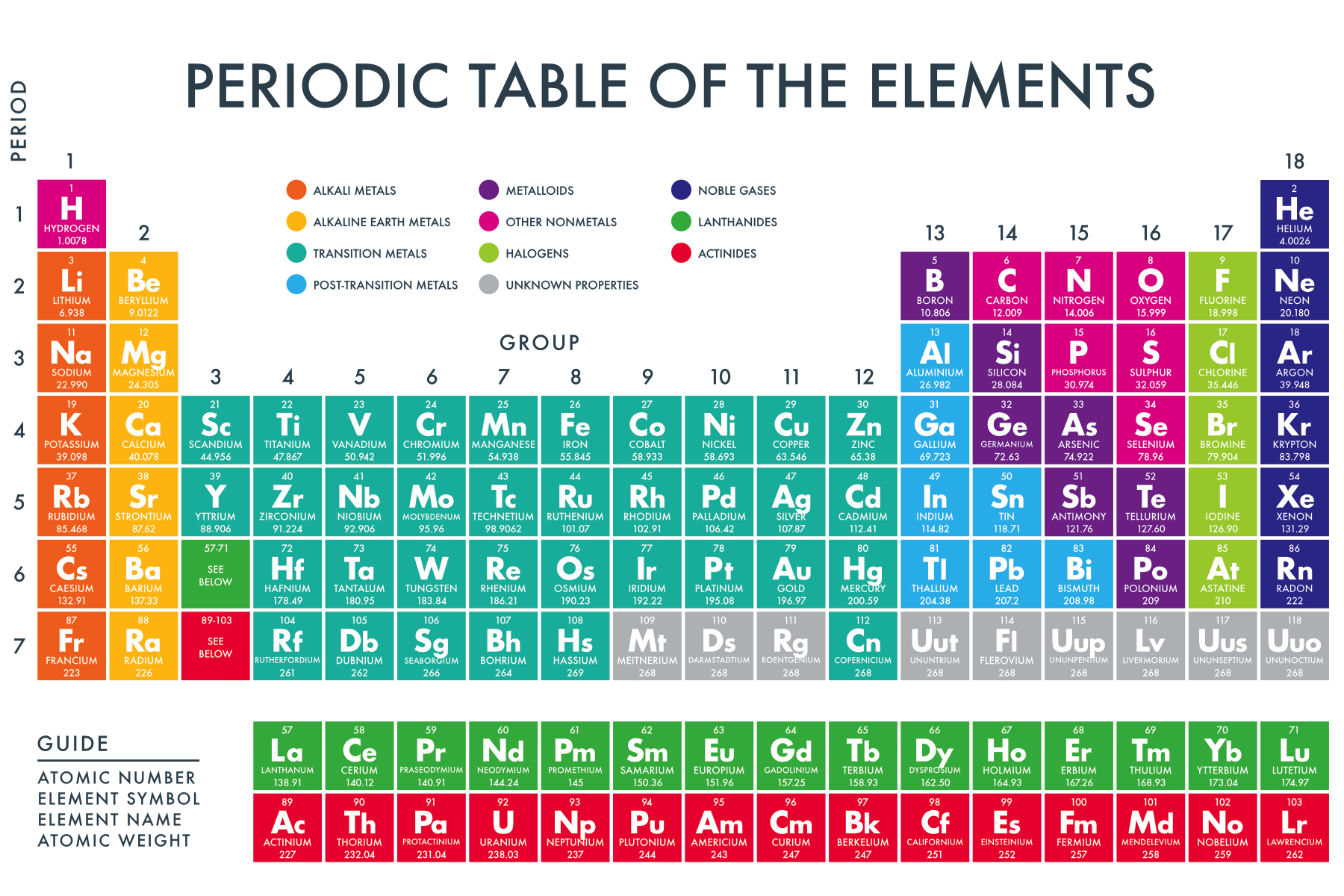
Group = elements in the same column
Period = elements in the same row
Each group has similar chemical properties
For example, Carbon belongs to group 14 so as silicon. Both can form up to 4 bonds.
Majority of elements are metals, i.e. conducts electricity and has shiny colors
| Group 1 | Alkali metals |
| Group 2 | Alkali Earth metals |
| Groups 3 - 12 | Transition metals |
| Groups 13 - 18 | Main group elements |
| Elements 57 - 71 | Lanthanides |
| Elements 89 - 103 | Actinides |
| Group 15 | Pnictogens |
| Group 16 | Chalcogens |
| Group 17 | Halogens |
| Group 18 | Noble gas |
Three States of Matter
Gas — No definite shape. Sparsely populated.Liquid — No definite shape. Viscosity.
Solid — Definite shape. High density.
Example: Steam = gas, water = liquid, and ice = solid
Properties of Substances
Two types:
- Physical property — change occurs w/o changing chemical compositions
Melting, boiling, density, solubility, among others
- Chemical property — changes arrangement of atoms in molecule
From carbon, such as the pencil lead and fluorine gas → C-F bond containing Teflon — very tough material used for coating on a cooking surface of a pan — resistant toward acid and base
Another way: Extensive vs. Intensive properties
- Intensive — independent of amount (or size)
Density, melting point, boiling point — good for ID
- Extensive — depends on amount (or size)
Mass, volume, energy
!!! One can make extensive property into intensive by by another extensive property.
| Mass (extensive) Volume (extensive) |
→ | Density (intensive) = Mass/Volume |
Measurement
In this class, all quantities measured follows the standard unit, called SI unit. The following table lists some of the important ones.
| Mass | kilograms | kg |
| Lenth | meter | m |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
| Amount of substances | mole | mol |
| Time | second | s |
| Electrical Current | ampere | A |
| Luminous Intensity | candela | cd |
Below is the picture of the instruments used in measuring volumes.
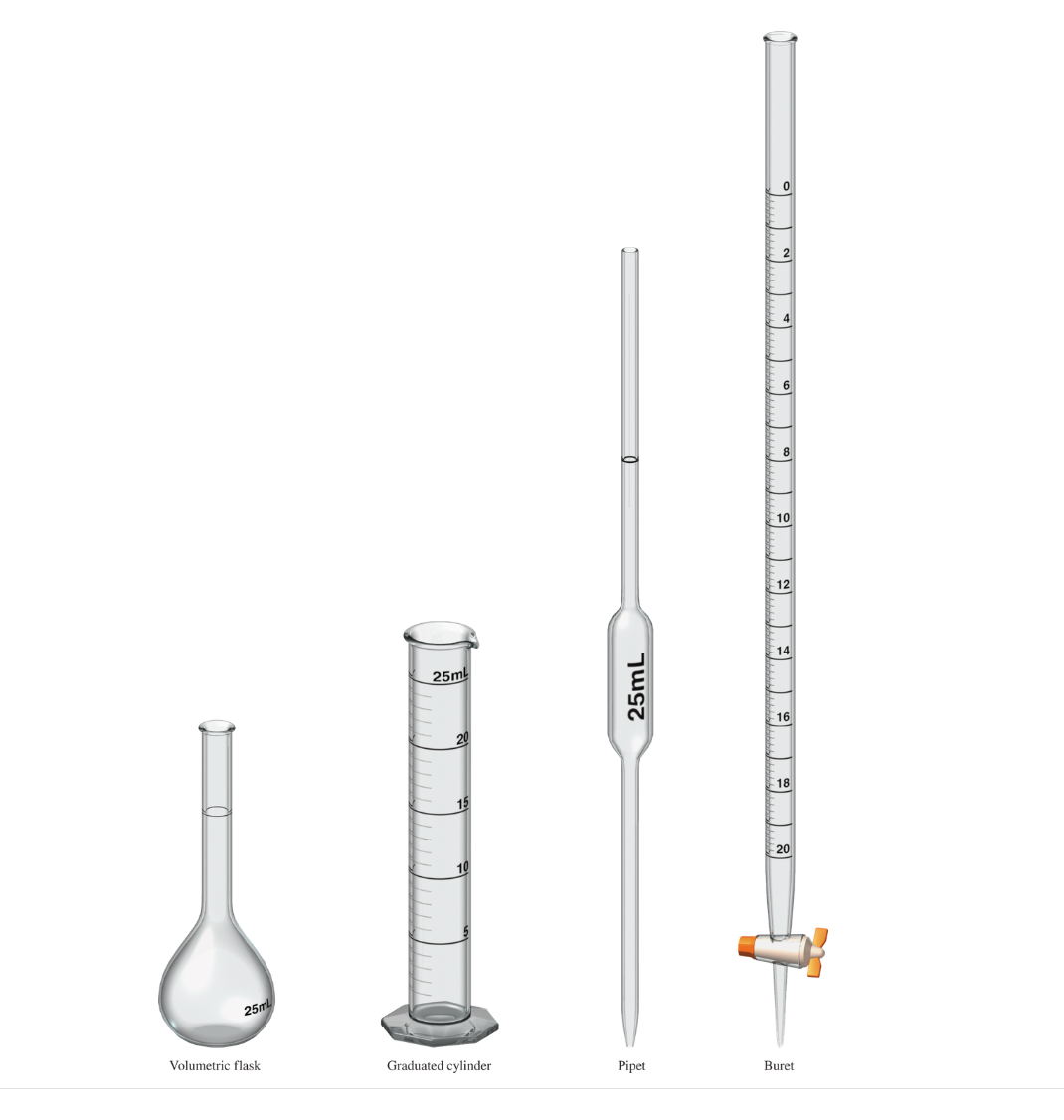

From left to right,
Volumetri Flask, Graduated Cylinder, Pipet, and Buret
Notice that there is no beaker! Because for measuring a volume, beaker
is not accurate enough!
Scientific notation — used to report measured values
It is quite nuisance to write a very large or very small number by using
all those zeros. For example, 0.000 000 888. This can be written compactly
by using scientific notation. 0.000 000 888 is expressed as 8.88 x
10-7. In this notation, it is said to have 3 significant digits
(these three numbers you have confidence in)
Prefixes for SI units
| Larger prefix | Smaller prefix | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yotta | Y | 1024 | deci | d | 10-1 | |
| Zetta | Z | 1021 | centi | c | 10-2 | |
| Exa | E | 1018 | milli | m | 10-3 | |
| Peta | P | 1015 | micro | μ | 10-6 | |
| Tera | T | 1012 | nano | n | 10-9 | |
| Giga | G | 109 | pico | p | 10-12 | |
| Mega | M | 106 | femto | f | 10-15 | |
| Kilo | k | 103 | atto | a | 10-18 | |
| Hecto | h | 102 | zepto | z | 10-21 | |
| Deka | da | 101 | yocto | y | 10-24 | |
Example: 1000 m = 1 km; 10 cm = 104μm, etc.
Below is a movie called "Powers of Ten" gives you perspectives on distance that span of 40 orders of magnitude! (The order is the number that is raised on 10. Thus, if you have the spans over 100 times or 102, then we say that it spans two orders of magnitude.)
Unit Conversion
Converting the measured values into another unit. In this course, we will delve into this subject much deeper than just a simple conversion, such as
- Conversion b/w mass: g → kg
- Conversion b/w length: mile → cm
- Temperature conversion: °F → °C
You can covert the temperature in the Celsius scale to what is known as the absolute temperature scale.
where K is called the Kelvin unit.
Example: What is the temperature at which both the Fahrenheight and Celcius scales have the same numerical value?
Since T(°F) and T(°C) are equal,
and using above equation, by substituting x, you get,
Now, solve for x. You get x = -40. Therefore, -40°C = -40°F.
We will come back to the unit conversion little later with a powerful technique, called Dimensional Analysis.
Energy
Definition of energy: Capacity to do work or supply heat.where w is the work, and q is the heat.
Another way, energy can be divided into kinetic energy, T, and potential energy, V, where with m = mass of object that is moving and its velocity is v.
The potential energy, V, is the energy depending on position. Intuitively, if I drop a ripe tomato from 30 cm in height vs. dropping from the roof of a building, you know you can get a bigger splatter by dropping from the rooftop. Before dropping, your tomato has potential energy (associated with gravity) that depended on the height.
Energy unit: we use joules (J) 1 J = 1 kg m2 / s2
Chemists like to use another unit of energy: calorie (cal) 1 cal = 4.184 J
Example: Which one has more kinetic energy, a 1400 kg car moving at 115 km/hr or a 12000 kg truck moving at 38 km/hr?
Calculate kinetic energy for both cases using In order to make the correct units, speed should be in the m/s unit. So, the car has more kinetic energy, but they are close!
Handling Numbers
There is always error associated with your measurement.
- Systematic error — inherent error, for example, in instrument
- Random error — imprecise measurement, for example, your shaky hands!
- Precision — degree of reproducibility
- How a series of measurements deviate from each other
- when deviation is small, it is said to be precise.
- Accuracy — how close a measurement is to the true value
Significant Figuers
Degree of condidence — meaningful # of digits in reported values
- Is it meaningful to say π=3.14159265359979? It really depends on how you carried out your measurement.
This is dependent on the number of digits that you are using in the calculations.
Before we move on, if the reported values appear as:
8.8 x 10-2 g, it is said to have two significant figures.
8.80 x 10-2 g, it is said to have three significant figures.
8.800 x 10-2 g is said to have 4 sig fig, and so on.
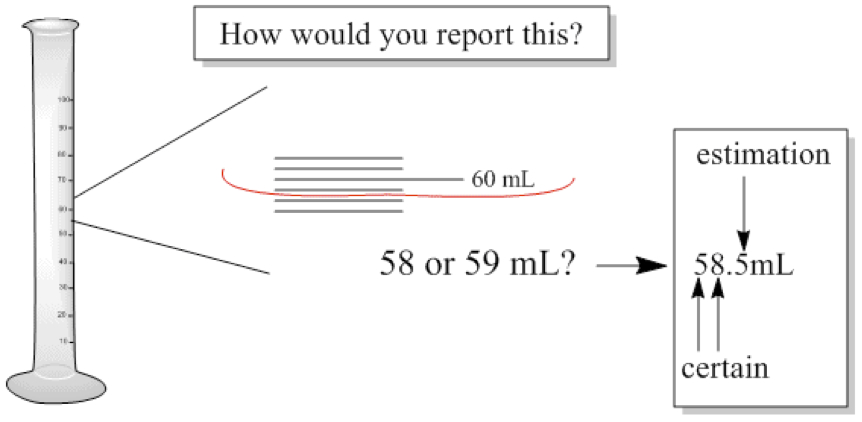
- If a reported value is 800 m, is it 800 m ± 1 m? ± 10 m?
- How would you report the following situation?
Significant figures in calculations
Multiplication and division — A x B = C. Use significant figure of whichever the smaller one (A or B) to the value of C.
Addition and subtraction — A - B = C. Use the smaller of the two decimal places of A or B in reporting C.
Rounding
If 0 - 4: If the first digit next to the last digit in the significant figure is 0 - 4, then remove all numbers smaller than the last significant digit.
- 2.4268 in 2 sig fig → 2.4
If 5 - 9: If the first digit next to the last digit in the significant figure is 5 - 9, then round up (add 1 to the last digit).
- 2.4268 in 3 sig fig → 2.43
Dimensional Analysis
Derived units — units that are composed of more than one fundamental unit. For example,
| Velocity | m/s | miles/hr |
| Density | g/mL | kg/cm3 |
| Concentration | mole/L | oz/gal |
| Volume is a special case | ||
| Volume | m3 | in3 |
We will do all kinds of conversions throughout this course. So, please follow closely!
We use dimensional analysis. The name of the game is to set up an equation such that you cancel out the given unit with conversion factors. It is more difficult to read it than to just do it!
The following figure shows the anatomy of dimesional analysis.
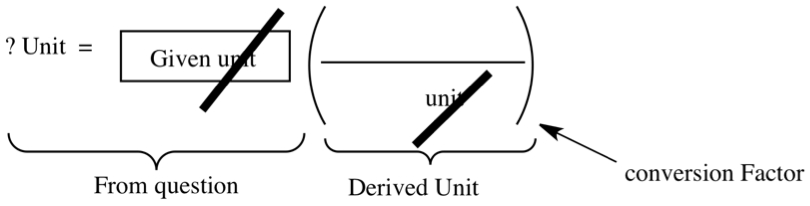
In this equation, the unit you are converting to appears on left with a question mark, and is equated to a certain given unit. In order for you to convert the given unit to desired one is to use a conversion factor, which usually comes from derived unit. If you place a right unit in the denominator in the parenthesis, you can cancel the unit with the given unit. By placing a unit in the denominator dictates what unit to put in the numerator.
Density and velocity are the typical examples of conversion factor. The former a has unit such as g/mL. Let's say that the density is 0.5 g/mL. It means for the purpose of dimensional analysis, 0.5g is equivalent to 1 mL. Or the speed limit on Major Deegan Expressway is 40 mi/hr in the Bronx. For our purpose, it has no deeper meaning, other than 40 mi is equivalent ot 1 hr. So, use derived units as your conversion factor.
Let's start with something very simple.
Converting length
Example:What is 5.7 m in cm?
Since 1 m = 100 cm according to the prefix table I gave you above, so each meter is 100 cm. In dimenstional anaylsis, you write down the question in the mathematical form as,
Now, you have to cancel the m with the denominator of the conversion factor, in this case 1 m = 100 cm. Then,
So far, so good. Right?
Let's try using density.
Example:Say that the density of some metal is 22.0 g/cm3. How many g are there in 30.0 cm3?
OK, the definition of density is d = m/v, but we don't really care if we know that or not. Since the unit is given as g/cm3, we can convert g to cm3 and cm3 to g; any way we want it.
In our case, we are looking for gram quantity given the volume of 30.0 cm3. So, we set up our equation as,
Since we need to cancel the cm3, we place cm3 of the density, and the leftover goes to the numerator (22.0g). Then,
Let's do little more complicated one.
Example:What is 570 cm in nm?
Again by using the prefix table, we know 1 m = 100 cm, and we know that 1 m = 109 nm.
As before we set up the equation as,
In order to cancel cm in the given unit, use use 1m=100cm conversion,
We now have m unit left on the numerator, which doesn't match with our goal of conversion to nm. So, we add another parenthesis so that
Now we are left with nm, which matches with the unit we're looking for.
All you need to do now is to compute the number.
How about this?
Example:How many miles are there in 320000 cm, if 1 mi = 1.609 km?
Since mile to km conversion is given, everything else can come from the prefix table.
to start our calculation. We have cm in the given, so 100 cm = 1 m, then m to km, then km to mi? Sounds like a plan,
Considering the fact that 320000 cm = 3.2 x 105cm, and the 105 would cancel with 100 and 1000 in the denominator, hence you only need to calculate 3.2/1.609, which give you the answer.
Let's try a difficult one.
Example:How many km are there in 1 light year. A light year is the distance that light travel in a year. The speed of light is 2.998 x 108m/s.
The difficulty is not in the conversion, but to think about what is equated to what initially. It is clear that we are looking for distance in km. Then, what is the given unit? Since we know the speed of light which convert distance and time. We are looking for distance, then the given must be in the form of time. Yes, we should equate km to 1 year for which light travels.
Then, I can set up the following,
What abut if we have the given to be the cube of the fundamental unit? In addition, the following question is very similar to Question 3 of the prelab in Density of Liquids and Solids lab.
Example:1.68 Vanillin is the substance whose aroma the human nose detects in the smallest amount. The threshold limit is 2.0 x 10-11g per liter of air. If the current price of 50 g of vanillin is $112, determine the cost to supply enough vanillin so that the aroma could be detected in a large aircraft hangar with a volume of 5.0 x 107 ft3.
We are going to start with identifying what we want to know, and which quantity to begein our calculation.
Real-World Problem Solving
Back of an envelope or order of magnitude estimation are used in real-life situations. These are the ball park figures of accurate numerical calculations. Such is useful when trying to figure out the desired value in the context of the discussion.
Using the example immediately above on how many km there are in 1 light year, we can see that 4*2*6*6*3 x 1013 in the numerator, and the denominator is 10-3. Thus combining the powers of 10, the value is 4*2*6*6*3 x 1010. So, 8*36*3 = 8*108 = 864 ≈ 900, and combining with the powers of 10, you get 900 x 1010 = 9 x 1012.